Sprained wrist - repetitive strain injury - carpal tunnel injury
Wrist injury
The wrist is made up of the two bones of the forearm (the radius and ulna) and eight carpal bones. Many ligaments connect these bones to each other.
Sprain
A sprain is an injury to the wrist ligaments without any evidence of bone injury (that is, no broken bones or cracks in the bone). With a sprain, there is usually only a partial tearing of the ligaments. In a severe wrist sprain, there can be a complete tear.
Strain
A strain is where there is a tearing of the muscle fibres in the area surrounding the wrist.
Fracture
A fractured or broken wrist means there is a break or a crack in one or more of the bones of the wrist. A severe fracture also causes damage to surrounding soft tissue, bruising, swelling and inflammation.
Repetitive strain
Repetitive use may result in an inflammation of the tendons (tendonitis). This is termed a repetitive motion injury and is not a true sprain.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is another common wrist injury that may occur from repetitive motion. It is a painful disorder of the hand caused by pressure on nerves that run through the wrist. Anything that aggravates and inflames the tendons can cause carpal tunnel syndrome, including repetitive hand movements, pregnancy and arthritis.
SportsMed TENS therapy for Wrist injuries
After a diagnosis of wrist injury, your management plan should include physical therapy treatment as often as possible.
SportsMed is the TENS, ECS and EMS machine we suggest to aid repair of a wrist injury.
SportsMed electrotherapy can be used everyday - between visits to the clinic - for drug-free, on-demand pain relief. It is also designed and programmed to aid circulation, reduce inflammation, hasten healing and help with muscle strengthening.
User guide
Please read the User Guide which comes with your TENS unit
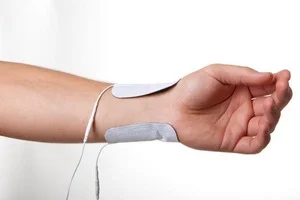
Pad placement - wrist injuries
Pain relief - place pads where they are comfortable and most effective for pain relief
Injury healing - pads are placed at the location of the injury
Muscle rehabilitation - the generic advice is to place one pad at the top of the muscle and the second pad one-third along the length of the muscle you wish to strengthen. You may need to consult your physiotherapist for specific guidance on which muscles to target.
If you have any questions please phone our office for further advice.